The OTC derivatives markets in the six emerging Asian economies – China, India, Indonesia, Malaysia, South Korea and Taiwan – are small and highly localized. While these six economies accounted for 61% of the total GDP, 68% of international trade, and 57% of equity trading in Asia in 2012, their share in OTC derivatives turnover was less than 10%.
In the report, OTC Derivatives in the Emerging Asian Economies, Celent analyzes the state of the OTC derivatives markets in six countries. Conservative regulations, lack of investor awareness, limited product universe, and the largely domestic nature of the financial markets have meant that the link between economic and financial activities is relatively low in these emerging economies. Although this has largely helped these countries in limiting the contagion of the financial crisis of 2008, the situation is slowly changing, as many of them take measures to liberalize their financial markets.
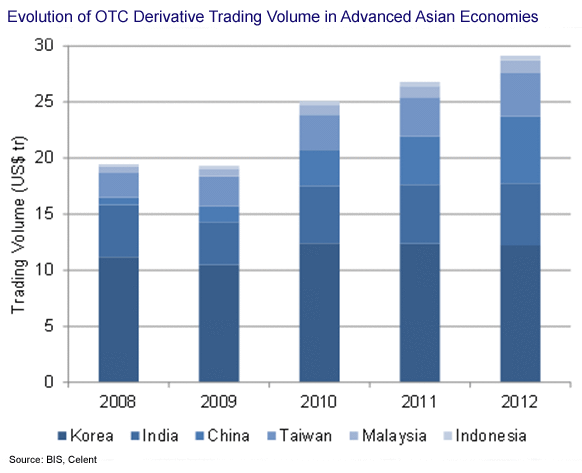
OTC derivatives trading volume in these countries reached US$29.1 trillion in 2012. South Korea is the leading market in terms of trading volume, followed by India, China, and Taiwan. Malaysia and Indonesia have very low OTC derivatives volumes, even by Asian standards. Foreign exchange derivatives are the dominant asset class in emerging Asian economies, accounting for 81% of total trading volume in 2012. Interest rate derivatives are a distant second, with an 18% share in total trading volumes. Other OTC asset classes have insignificant volumes, as most of the emerging economies either do not allow or do not have the necessary infrastructure for trading other OTC derivatives products.
Foreign banks play a major role in the OTC markets of these emerging economies. Their superior capabilities in terms of products and processes, as well as their experience in Western markets in this segment, give them an edge over domestic banks.
“Developments in Asia’s emerging economies will contribute to the growth of OTC activity in the advanced countries, particularly in Hong Kong and Singapore,” says Arin Ray, Analyst with Celent’s Securities & Investments Group and author of the report. “Presently, many corporates in these emerging economies trade at international exchanges or with international counterparties because of the lack of opportunities in their domestic markets.”
This report discusses recent market trends in the OTC derivatives segments of Asia’s emerging economies. It delves into issues at a national level for each of the six countries. The report also analyzes differences between the OTC markets in developed and emerging Asian economies.





