Payments Systems Trends in Japan, Part III: Blueprints for the Next-Generation Zengin System
Abstract
In the report Payment System Trends in Japan, Part 3, Celent examines initiatives to accelerate the development of Japan’s payment infrastructure through the lens of the Zengin System. This report distills how cutting-edge technology is being applied and imagines the evolution of the financial services landscape as we enter the brave new world of Fintech.

Following the launch of the 6th Generation Zengin System, the Bank of Japan has continued to discuss and search for ways to improve Zengin Net. In December 2014, the JBA and Zengin Net released deliberation results on the Zengin System. The document called for expanded hours of operation, articulated concrete policy, and described the current state of awareness of financial electronic data interchange (EDI) in the financial industry.
Furthermore, in December 2015, the Financial Services Agency’s Financial System Council released the “Strategic Initiative for Advancements in Payments and Transaction Banking.” In the segment on payment infrastructure, the report put forth five reforms hinging on the Zengin System. It also called for fundamentally enhancing features of the payment infrastructure as well as realizing one common and integrated payment environment that caters seamlessly to both domestic and overseas transactions, and it spelled out a clear deadline for migrating from legacy environments.
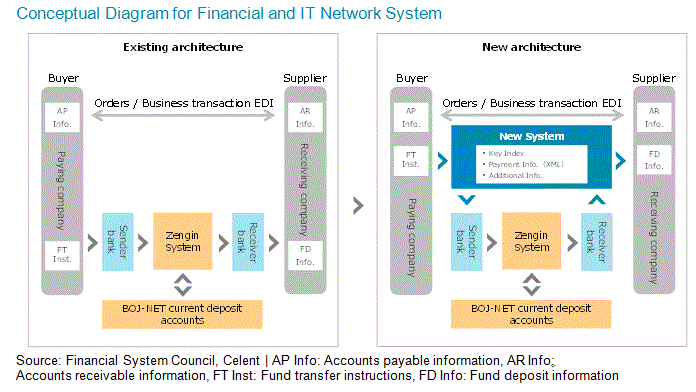
“We would like to put forth the concept of an open innovation platform to realize a platform layer and innovation layers. The expectation is that the conceptual system could fulfill the role of an application programming interface provider in the era of the API economy,” says Eiichiro Yanagawa, a senior analyst with Celent’s Asian Financial Services practice and author of the report. “When envisioning the financial services of the future, one must imagine services that transcend the traditional confines and that are more intimately intertwined with corporations and their activities as well as the lives of consumers.”
Part 1 of this report series provides an overview of global payment trends, reviewing the history of Japan’s payments system and concluding with an evaluation of the performance measures in place at the time of the financial crisis and an outlook for the future. Part 2 explores the next-generation Bank of Japan Net (BOJ-NET) Funds Transfer System, discussing national initiatives to build a sustainable and robust payments system in addition to looking at payment services providers.
This 21 page report contains 6 figures.

